When an organisation decides to use a permanent test organisation, a process is started to create that organisation.
Setting up a permanent test organisation involves six activities that are described below. Setting up a permanent test
organisation represents an organisation change. A new organisational unit is created, and in some cases this means that
people have to switch departments, with consequences for their tasks, authorisations and responsibilities. As such, the
execution of the general activities relating to organisation changes (e.g. tuning with the Works Council) will have to
be taken into account in addition to the six activities. All this makes setting up a permanent test organisation a
long-term process that may take months or even years.
Activities
The migration process to switch from the existing situation to a permanent organisation involves six
activities:
-
Inventory
-
Definition
-
Organisation
-
Awareness
-
Trial
-
Implementation
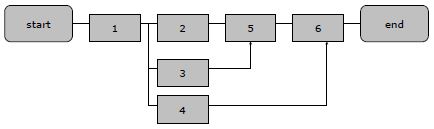
The diagram in figure 1 - Setting up a test organisation shows the overall order of and dependencies between
the various activities.
Method of operation
A preliminary study is done when there is an interest in setting up a permanent test organisation. A preliminary study
proposal is created that indicates how to clarify the issue, the direction in which a solution can be found, and the
content. Subjects are a feasibility study, organising a session, and use of the service matrix. The proposal contains
an overview of the stakeholders in this activity, plus an overall time estimate and planning. The preliminary study
ends with a plan of approach for setting up the test organisation, on the basis of which the project board can make a
go/no go decision for the follow-up process. The plan of approach for setting up the organisation is complete at the
end of the preliminary study. It contains an overall overview of the 5 other activities and an estimate of the lead
times. It describes the activities definition (with as important product the process description), organisation, trial,
awareness and implementation. The plan of approach also contains a proposal for the trial project. This project ends
with a report, on the basis of which the project board can make a go/no go decision for the implementation activity.
During the implementation, the organisation set up for a trial project is adjusted if necessary and implemented in the
organisation in an increasingly broadly-based manner.
|
